
What is Continuous Training? (with pictures)
To lower the disease risk, continuous endurance training (CET) such as running, brisk walking or cycling at moderate intensity is the recommended exercise modality, including 150-250 min•wk-1 activity ( Donnelly et al., 2009 ).

PPT How does a marathon runner use aerobic endurance? PowerPoint Presentation ID2464427
ek high-intensity interval training (HIIT) intervention, or an isocaloric continuous endurance training (CET) intervention on insulin resistance indices and change in irisin and preptin in patients with prediabetes. Thirty-two prediabetic male patients (age = 38.7 ± 4; body mass index = 26.9 ± 1.4 kg·m−2; and V̇o2peak = 2.49 ± 0.22 L·min−1) were randomly assigned into 3 training.

Top 10 Benefits of HighIntensity Interval Training • Bodybuilding Wizard
Continuous training is a form of exercise that is performed at a 'continuous' intensity throughout and doesn't involve any rest periods. Continuous training typically involves aerobic activities such as running, biking, swimming and rowing. These activities use large muscle groups performing repetitive movements over a prolonged period of time.
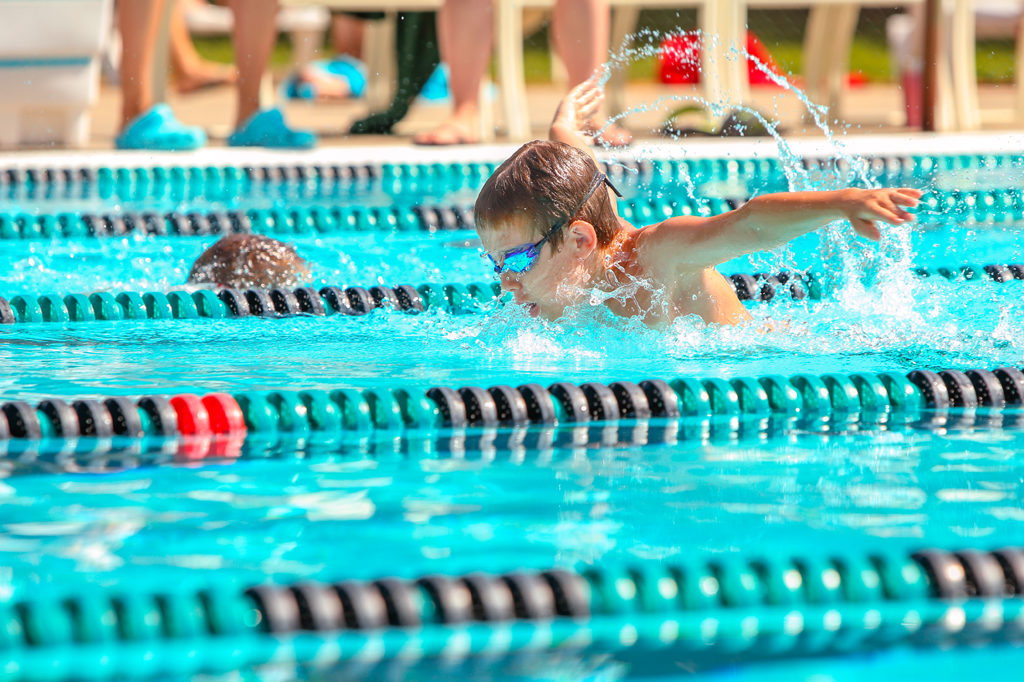
Forms of endurance training FitnessIndex
Adaptations to Endurance and Strength Training. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med2018 Jun 1;8 (6):a029769. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029769. The capacity for human exercise performance can be enhanced with prolonged exercise training, whether it is endurance- or strength-based. The ability to adapt through exercise training allows individuals to.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/13681265/shutterstock_1007038000.jpg)
How Does Continuous Training Improve Cardiovascular Fitness All Photos Fitness
The ability to adapt through exercise training allows individuals to perform at the height of their sporting event and/or maintain peak physical condition throughout the life span.

How Does Continuous Training Improve Cardiovascular Fitness All Photos Fitness
High-intensity interval training imparts the same or greater benefits to the general population as continuous endurance training, namely, in improving V O 2max, quality of life, and metabolic health, among others.

Personal Exercise and Fitness Notes Physical Education Leaving Cert iRevise
A 2019 study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that a 12-week strength training program improved maximal oxygen uptake (VO2 max) in recreational runners. The researchers found that the strength-trained group had a 5.7% increase in VO2 max compared to the control group that did not perform strength training.

HIIT vs. Continuous Endurance Training Battle of the Aerobic Titans Yoga lesson plans
The aim of the study was to examine the effects of two different training programs (high-intensity-training vs. continuous endurance training) on aerobic power and body composition in recreationally active men and women and to test whether or not participants were able to complete a half marathon after the intervention period.
(PDF) Comparison of sprint interval and continuous endurance training on oxidative stress and
HIIT has been proposed to be equal or advantageous to continuous endurance training both in terms of physiologic results [7, 8] and in enjoyability . However, the health benefits, risks, and optimal design of HIIT are still unclear. Further, most of the research on the effects and benefits of HIIT has been done in younger and middle-aged adults.

ENDURANCE CONTINUOUS OR INTERVAL TRAINING?
These groups were matched based on the required energy expenditure (EE) for completing each protocol: (a) HIIT (10 × 60 seconds at 90% peak oxygen uptake [V̇o2peak], 1: 1 work to recovery at 50 W), (b) CET at an intensity equivalent to maximal fat oxidation (Fatmax) (CETFAT) (pedaling for a duration that expends an equivalent EE to an HIIT sessi.

2400 CONTINUOUS MOVES for MUSCULAR ENDURANCE workout / LOWIMPACT, NO REPEATS! Good change of
Consistent endurance exercise—such as 30-60 minutes of continuous running or cycling 3-7 days a week—causes a long list of cardiovascular adaptations and responses (see Figure 1). HIIT vs. Continuous Endurance Exercise: HIIT vs. Continuous Endurance Exercise: Cardiovascular Adaptations

Training Principles1
Both forms of interval training induce the classic physiological adaptations characteristic of moderate‐intensity continuous training (MICT) such as increased aerobic capacity ( V ˙ O 2 max ) and mitochondrial content.

HIGH INTENSITY OR CONTINUOUS ENDURANCE TRAINING PERFORMED TO PREVENT PREDIABETES ACE Physical
Background Enhancing cardiovascular fitness can lead to substantial health benefits. High-intensity interval training (HIT) is an efficient way to develop cardiovascular fitness, yet comparisons between this type of training and traditional endurance training are equivocal. Objective Our objective was to meta-analyse the effects of endurance training and HIT on the maximal oxygen consumption.

12 Crazy Battle Rope Exercises for HighIntensity Interval Training Rope exercises, Battle
Continuous training is one factor involved in Cardiorespiratory Endurance with the further training methods of Interval Training and Fartlek Training also playing a major role in this important conditioning. Cardiorespiratory; heart and lungs, and their ability to deliver the efficient supply of oxygen to the muscles during periods of sustained.

Training methods
Consistent bouts of endurance exercise such as 30-60 minutes of continuous running or cycling performed 3-7 days per week leads to several other cardiovascular adaptations including the following: 1. Increased cardiac muscle mass 2. Increased stroke volume 3. Increased disposal of metabolic wastes 4. Increased oxidative enzymes and efficiency 5.

PE Poster Top 10 Cardiovascular Endurance Exercises Cardiovascular endurance exercises
With endurance training, the primary aim is to convert stored fat into energy, a process that requires a lot of oxygen (referred to as aerobic metabolism). HIIT, by contrast, uses both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism to generate energy for workouts.